Enzyme Kinetics
Problems for Classroom Discussion
Gale Rhodes
Department of Chemistry
University of Southern Maine
Portland, Maine 04104-9300
Revised 2006/07/14
Enyzme Kinetics and Inhibition: Example for Analysis in
Class
(Data taken from Lindquist, R.N., Problems and Solutions Guide to
Accompany Rawn's Biochemistry, Neil Patterson Publishers, 1990.)
The table gives enzyme-catalyzed reaction rates (initial rate,
V0) measured at various substrate concentrations in
solutions with [E] = 1.2 x 10-4 mmol/L.
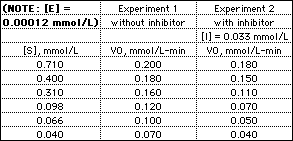
- Use the data from Experiment 1 to calculate
Vmax (in mmol/L-min), Km (in mmol/L), and
kcat (in sec-1) for this enzyme-catalyzed
reaction.
- Use the data from Experiment 2 to determine the apparent
Vmax (in mmol/L-min), and Km (in mmol/L) in
the presence of the inhibitor. From this information, determine
the type of inhibition (competitive, noncompetitive or
uncompetitive) and calculate the dissociation constant
KI for the inhibitor. For help, see Summary
of Kinetic Effects of Reversible Inhibitors.
An answer link will appear on the calendar after we discuss the problems in
class.
Handing In Solutions To These Problems
If you are offered the opportunity to hand in solutions to these
problems for grading, your solution for each question should
include
- a printed graph from Excel (or other graphing program), with
equation and correlation coefficient of line fitted to data;
- complete calculations, with units of all quantities, resulting
in the answers expressed in proper units, and with proper
significant digits.
Goodies
Biochemistry
Resources

